Nightfall AI, a startup providing cloud data loss prevention services, today announced that it raised $40 million in Series B financing from investors including WestBridge Capital, Venrock, Bain Capital Ventures and — for some reason — athletes and celebrities including Paul Rudd, Drew Brees and Josh Childress. CEO Isaac Madan says that the proceeds will be put toward doubling Nightfall’s 60-person headcount, scaling the platform to more customers and markets, and expanding Nightfall’s partner ecosystem.
Madan founded Nightfall in 2018 alongside CTO Rohan Sathe. Isaac was previously a VC investor at Venrock, where he focused on early-stage investments in software as a service, security and machine learning. Rohan was one of the founding engineers at Uber Eats, where he designed and built software to grow the platform’s footprint.
Madan says he and Sathe were inspired to launch Nightfall by Sathe’s personal experiences with data breaches arising from poor “data security hygiene.” Sathe was at Uber in 2016 when a developer committed credentials to a private code repository on GitHub, leading a hacker to extract Uber rider and driver data to a public storage service.
“This breach made it clear that attackers will eventually find ways into private applications, so it’s crucial to ensure strong data security hygiene to minimize risk once a bad actor gets in,” Madan told TechCrunch in an email Q&A. “Digital transformation and the shift to a hybrid workplace has eroded the traditional corporate perimeter as it’s no longer guaranteed that employees are on managed devices and networks. This has led to the proliferation of cloud applications that house data that is completely opaque to security teams and increases the attack surface area.”
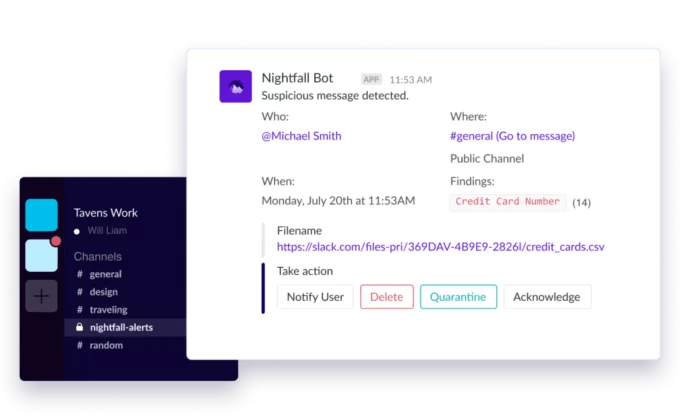
Image Credits: Nightfall AI
Nightfall’s platform monitors data flowing into and out of apps like Slack, Salesforce, Google Drive, Confluence and Jira, which machine learning algorithms classify as sensitive, personally identifiable (PII), noncompliant (with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR), or safe to share. From a dashboard, admins can set up automated workflows for quarantines, deletions and more, or view metrics like real-time and historical PII count by type.
Nightfall offers pretuned PII detectors out of the box that can spot things like compromising keys in GitHub repositories, credit card numbers, names, locations, phone numbers, Social Security numbers and even cryptocurrency wallet addresses. Exposed through an API and a software development kit, Madan claims that Nightfall’s data classification tech can be applied to just about app or service.
“[We’ve] launched partnerships with Snyk, Cribl, Virtru, Hanzo and more to expand our partner capabilities by embedding Nightfall’s detection capabilities into their offerings,” Madan said. “Organizations today manage high volumes of sensitive data, spanning credentials and passwords, PII, protected health information, and much more … [With Nightfall, they can] take action on sensitive data at a granular level, get full context on violations, and automate response, coaching end-users to fix issues or self-remediate.”
Potential Nightfall customers might be put off by the platform’s data policy, which permits Nightfall to use their data to “continually improve [its] data classification algorithms.” Meanwhile, employees might be concerned about the surveillance potential; one of the use cases Nightfall advertises on its website is scanning chat tools (e.g. Slack) for disallowed content.
The company suggests its platform can limit toxicity and profanity, but algorithms historically haven’t done a great job at this. More problematically, Nightfall promotes “insider threat” prevention features that could in theory be used to target whistleblowers.
During the pandemic, various forms of workplace monitoring came into wider use — enabled by the transition to remote and hybrid work setups. One market research company estimates that 60% of large enterprises now have some kind of tool to track workers remotely. Employees have pushed back, however. According to a 2021 ExpressVPN survey, close to a majority believe that monitoring software — which is largely legal in the U.S. — is a violation of trust and would consider quitting a company that used it.
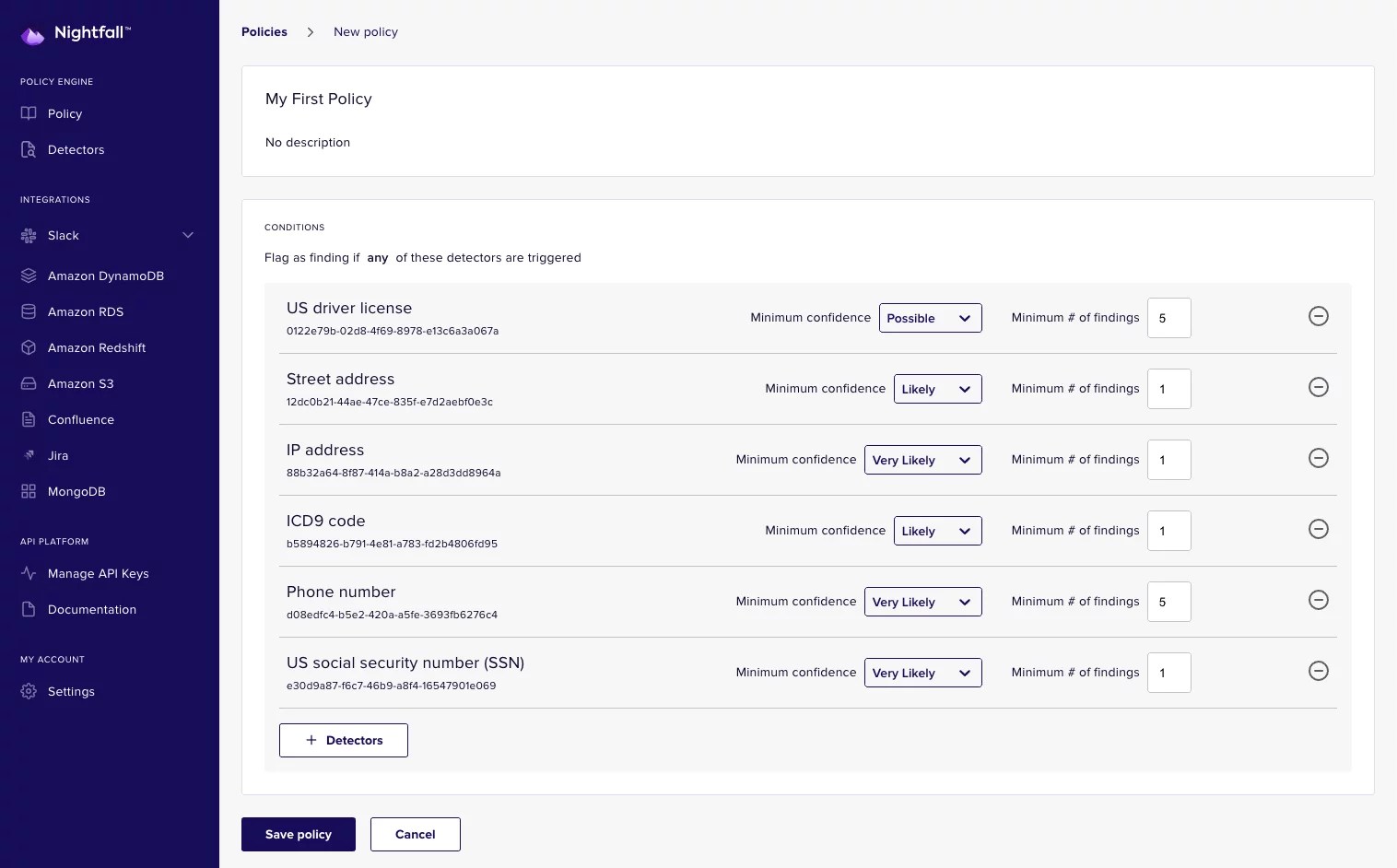
Image Credits: Nightfall AI
Madan didn’t respond directly to a question about employee privacy. But he claims companies have the choice of not sharing any data with Nightfall; those that do can request that their data be deleted.
“Given the sheer volume of data and the rapid growth in the number of cloud applications in the enterprise, data sprawl is pervasive, and getting worse,” Madan said. “The shift to a hybrid workplace has eroded the traditional perimeter, and organizations must focus on applications and services in their environment that house sensitive data — their crown jewels.”
While Nightfall competes against well-funded startups including Netskope, Very Good Security and Bitglass in the multibillion-dollar data loss prevention market, the company has managed to attract customers including Klaviyo, UserTesting and Rightway and “hundreds” of others since its founding. The private sector makes up the whole of Nightfall’s current customer base, but Madan said that he’s “open” to government and military clients in the future — reflecting the money to be made from cybersecurity in the defense industry.
When reached for comment via email, Bain Capital Ventures partner and Nightfall board member Enrique Salem said: “Data security is quickly becoming the most critical and vulnerable layer of an organization’s security stack. Nightfall is the emerging leader in cloud DLP, protecting organizations from costly data leaks and enabling strong data security hygiene without blocking business users.”
To date, Nightfall — which is based in San Francisco — has raised $60 million in funding and scanned over 40 million “sensitive data findings,” Madan added.






