Perpetual futures are a unique type of derivative contract in the cryptocurrency market. Unlike traditional futures contracts, which have a set expiration date, perpetual futures can be held indefinitely. This makes them a crucial instrument for traders looking to speculate on the future price of Bitcoin without the constraints of a fixed timeline.
One of the key mechanisms that govern the operation of perpetual futures is the funding rate. This is a small fee paid between long and short position holders, designed to keep the price of the perpetual futures contract in line with the underlying spot price of Bitcoin.
The funding rate is essentially a periodic payment, typically made every eight hours, that is transferred from one group of traders to another.
When the price of the perpetual futures contract exceeds the spot price, the market is in a state known as contango. In this situation, the funding rate becomes positive, and traders who hold long positions (those who have bought the contract expecting Bitcoin’s price to rise) are required to pay a fee to traders with short positions (those who have sold the contract expecting the price to drop). This fee acts as a disincentive for holding long positions, thereby exerting downward pressure on the futures price to bring it back in line with the spot price.
Conversely, if the futures price is lower than the spot price, the market is in a state called backwardation. In this case, the funding rate turns negative, and traders holding short positions have to pay the fee to those with long positions. This dynamic encourages traders to either close their short positions or open long positions, which in turn pushes the futures price upwards toward the spot price.
By continually adjusting the funding rate based on the disparity between the futures and spot prices, exchanges can effectively ensure that the price of Bitcoin perpetual futures remains close to the spot price. This mechanism is vital for maintaining market stability and preventing significant price discrepancies that could lead to arbitrage opportunities. Furthermore, the funding rate serves as a valuable indicator for traders, providing insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
The funding rate for Bitcoin perpetual futures experienced a significant spike in August. The rate increased from 0.006% on July 31 to 0.009% on August 1, marking a 50% jump. Since then, it has remained steady at 0.009%.
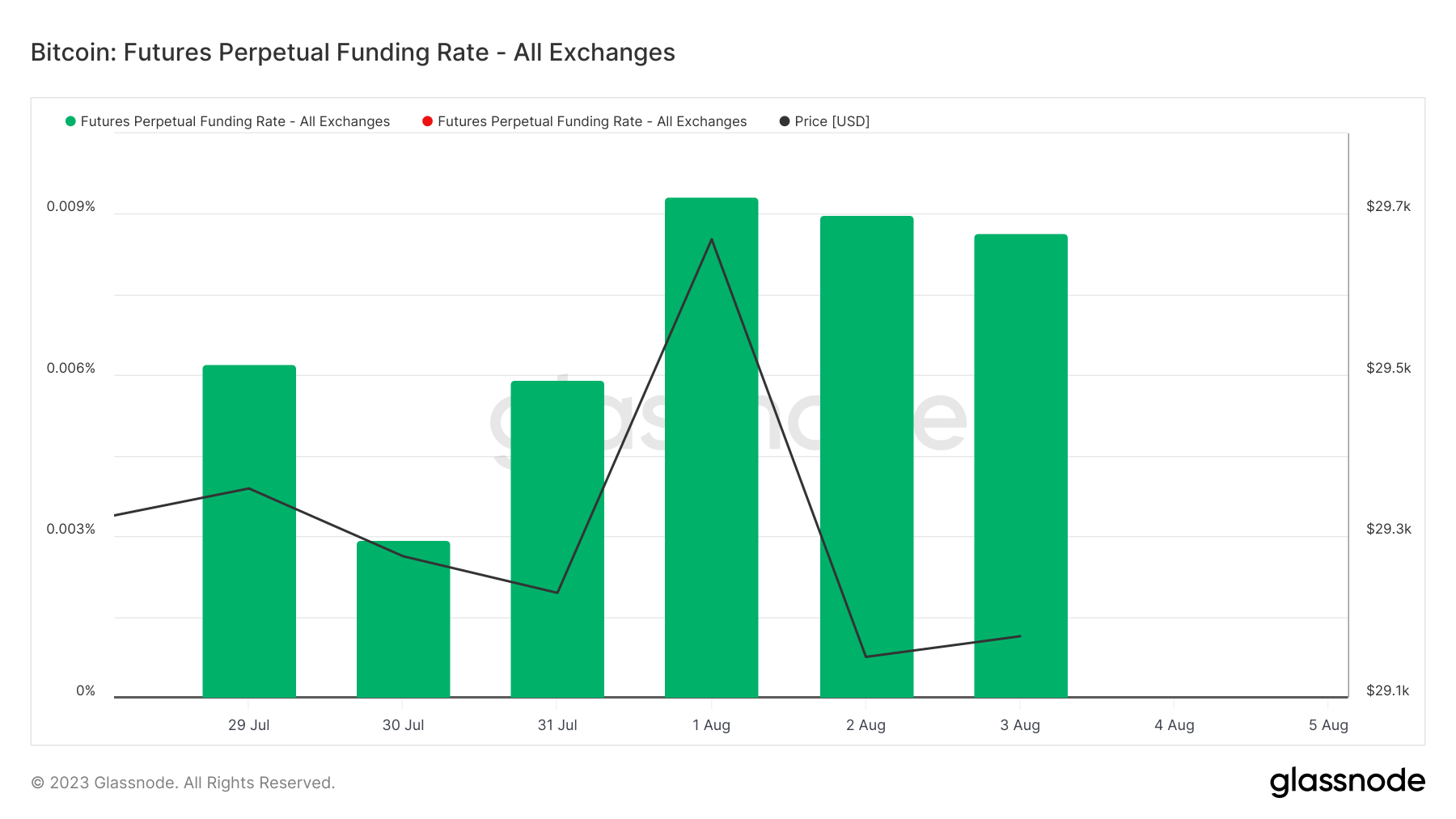
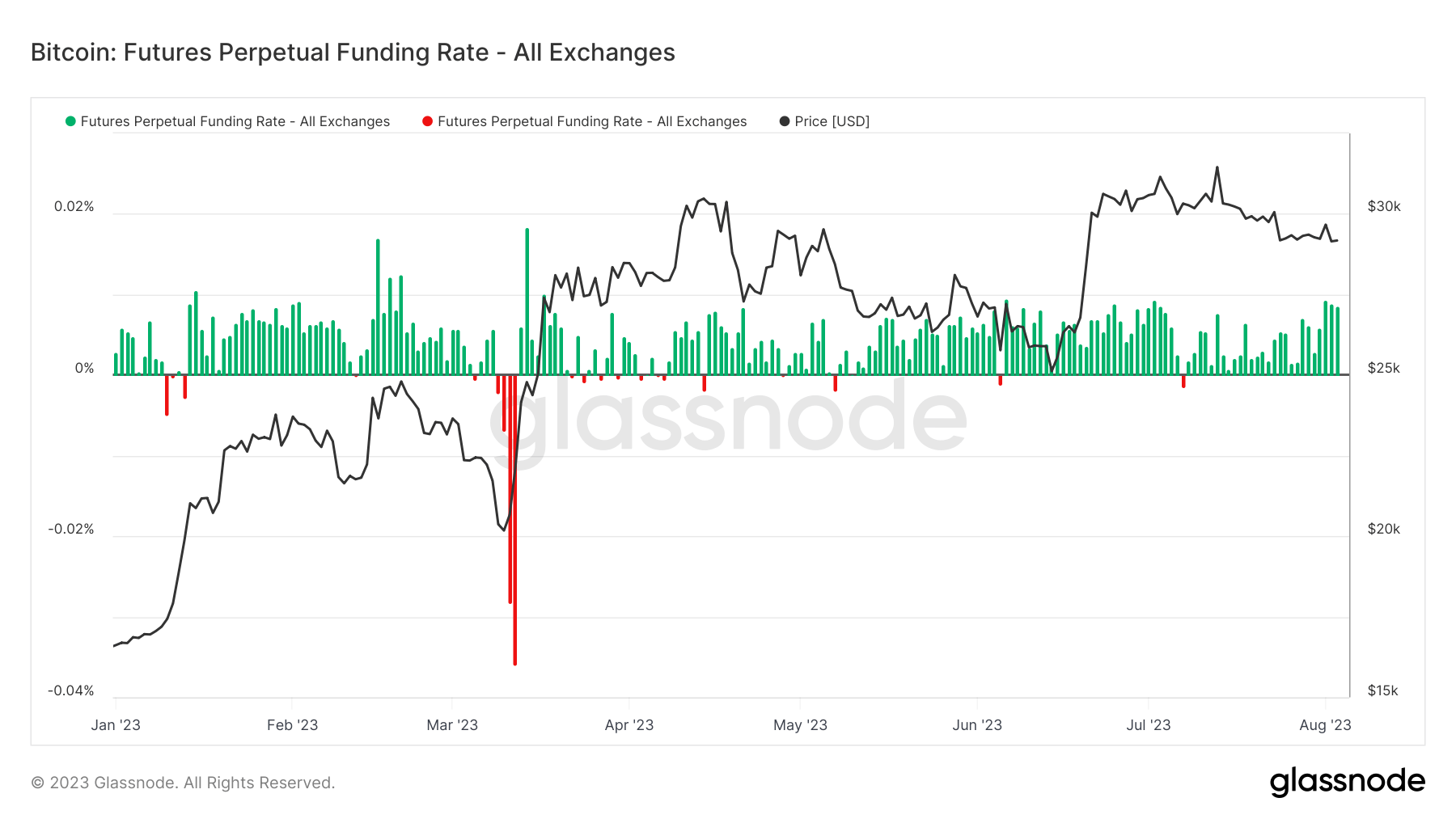
Historically, significant movements in Bitcoin’s price have often been accompanied by spikes in the funding rate. The recent increase coincided with Bitcoin’s price jumping to $29,668. A broader view of the market reveals frequent correlations between spikes in the perpetual futures funding rate and price movements.
A closer look at the funding rate across various derivative exchanges reveals that the largest spike was seen at Binance. The funding rate at this exchange increased by a staggering 100%, jumping from 0.005% on July 31 to 0.01% on August 1. Other exchanges also witnessed notable increases, while Bitfinex was the only platform where the perpetual rate decreased, falling by 25%.
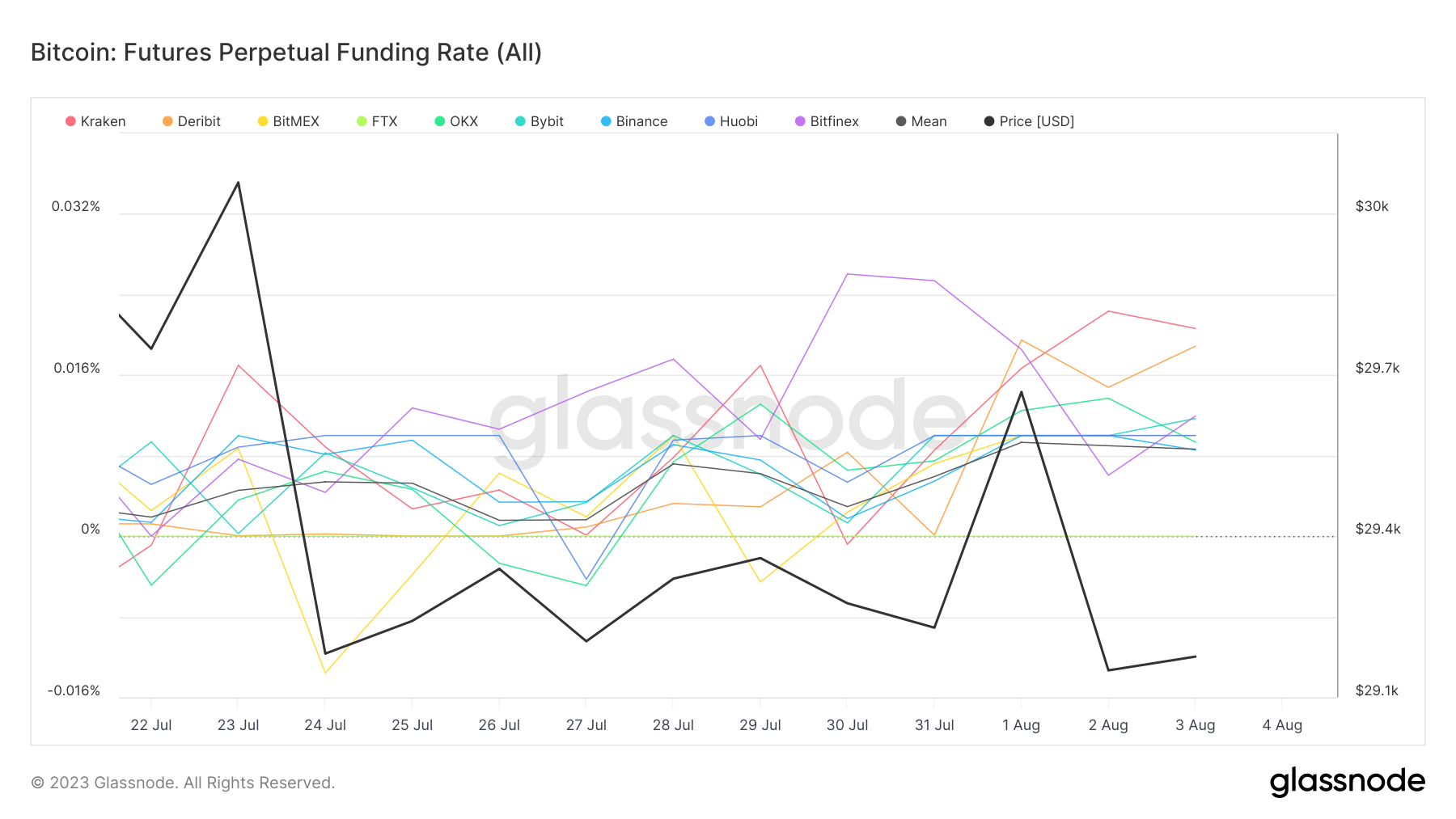
This surge in the funding rate has significant implications for the Bitcoin market. It indicates a bullish sentiment among traders, as a higher funding rate typically suggests that the price of the perpetual futures contract is above the spot price. However, it also increases the cost of maintaining a long position, which could potentially lead to a decrease in long positions if traders are not confident that the market will continue to rise.
The post Bitcoin perpetual futures funding rate soars in August: Here’s what this means appeared first on CryptoSlate.









