Qase, a Austin-based platform for managing software quality assurance testing and reporting, today announced that it raised $7.2 million in a Series A round led by Chrome Capital with participation from Finsight Ventures and S16VC.
Nikita Fedorov, the CEO and founder, says that the proceeds will be put mostly toward product development, including a plug-ins marketplace, and expanding Qase’s 33-person workforce to 50 by the end of the year.
“This expansion will enable us to accelerate our R&D and better serve our increasing user base,” Fedorov told TechCrunch in an email interview. “It’ll ensure that our platform remains at the forefront of innovation, meeting the evolving needs of our users.”
Fedorov, who got his start in software engineering as a PHP developer, was inspired to launch Qase after working as the head of billing and payment systems for Avito, a classified ads site. While there, he faced a niggling problem: he couldn’t find a test management system that wasn’t solely focused on manual, as opposed to automated, testing.
“The software testing tools market faces significant challenges, including a crowded and fragmented landscape,” Fedorov said. “Companies often rely on multiple tools, ranging from ten to 40, for their daily testing needs — which can lead to inefficiency. Moreover, the industry struggles with a low ratio of test automation, indicating an ongoing dependence on manual testing.”
Indeed, companies often struggle to find the right set of tools to execute their software testing strategy. In a recent survey from Kobiton, an app testing platform, 26% of organizations said that finding tools for test automation was the biggest challenge they faced.
The cost of bugs is enormous, though — adding to the pressure on companies to find testing tooling. One report suggests that 26% of the average developer’s time is spent reproducing and fixing failing tests, which equates to 620 million developer hours a year. That’s not to mention, of course, the effects on a company’s reputation when serious bugs slip into the wild.
Over the course of two years while working at Avito, Fedorov built an MVP for Qase. In 2018, he launched it in early access, and in 2020, he quit his day job to work on Qase full time.
According to Fedorov, Qase was built around three core pillars: test management, test reporting and test analytics. Intended to serve as a single platform for manual and automated testing, Qase, which integrates with a number of popular software testing frameworks and supports third-party tests, can collect test execution results for manual and automated testing — providing analytics throughout the process.
Wait, you might ask — aren’t there plenty of software testing suites out there? Well… yes. There’s ProdPerfect, which focuses on automated web app testing, and SpotQA, an automated software testing platform that claims to be significantly faster than its competitors. There’s also Virtuoso, a startup that uses machine learning to identify software bugs and errors.
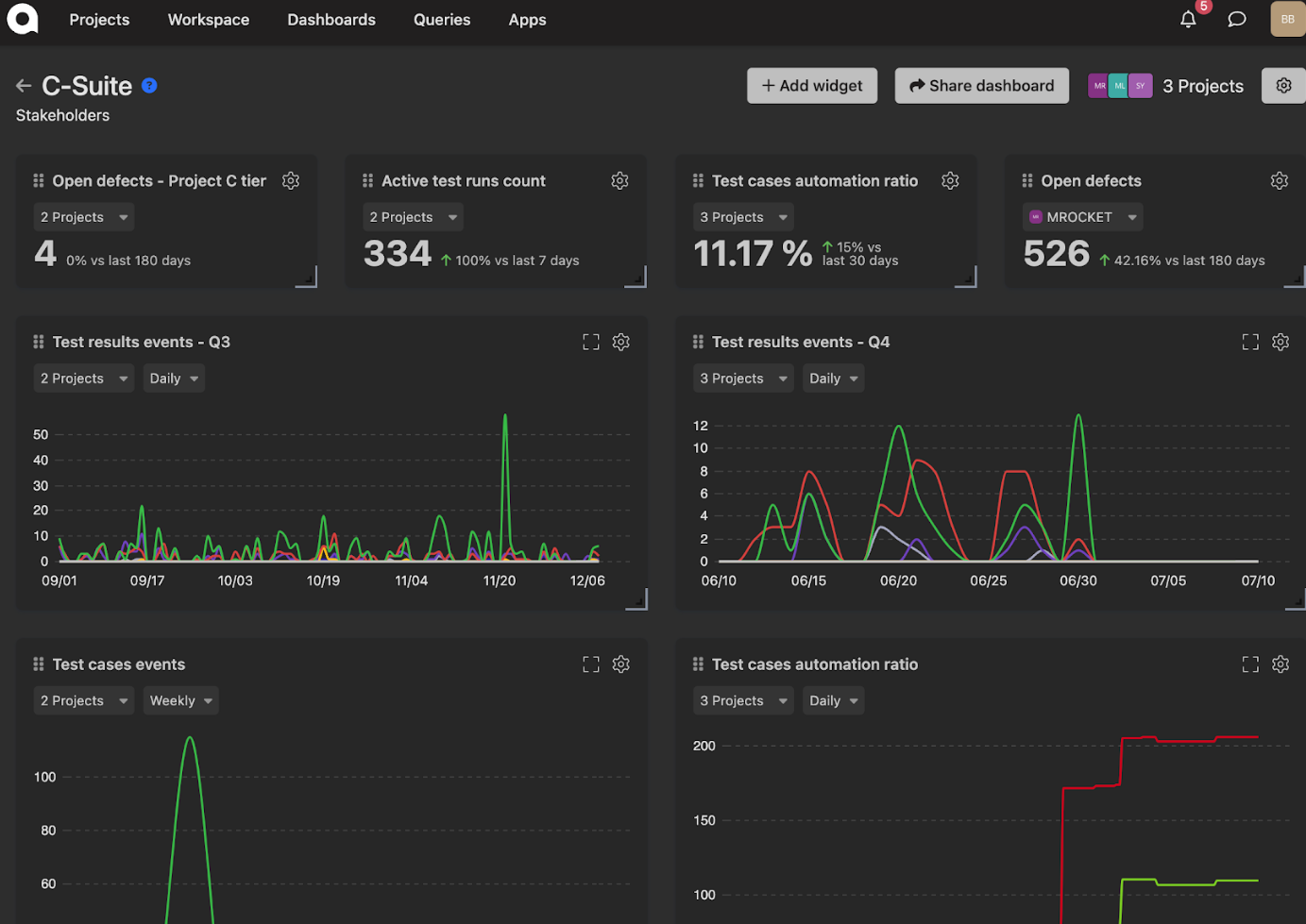
Qase’s automated and manual test reporting dashboard.
But Fedorov claims that Qase’s advantage lies in its “comprehensive organizational view,” a feature that encourages a more holistic approach to software testing. Within Qase, testing reports and dashboards can be shared among teams. And Qase syncs tests not only with ticket trackers but other testing frameworks and Ci/CD tools, organizing the results by severity and priority.
“Qase’s technology holds immense significance for data and technical decision makers, particularly at the C-suite level,” Fedorov added. “As an integral part of the software development lifecycle, software testing plays a key role in reducing time-to-market. This efficiency optimization directly affects the bottom line, making it a top priority for enterprise organizations seeking a competitive edge.”
It sounds a little like marketing jargon to this writer. But Qase has had impressive uptake, to be sure — managing to bring its annual recurring revenue to $2 million within three years. In the last six months alone, Qase has identified over a million bugs for 100,000 users and enterprise customers including Asana, SeatGeek and Doordash-owned Wolt.
“We’re focused on maintaining a sustainable financial foundation. Our operating cash flow results demonstrate a stable financial position,” Fedorov said. “While the tech industry has experienced a slowdown over the past year, we’re positioned to navigate potential headwinds by transitioning to a ‘pay-per-usage’ business model. This strategic shift, coupled with our value-driven approach, ensures that customers pay for the actual benefits they receive.”






