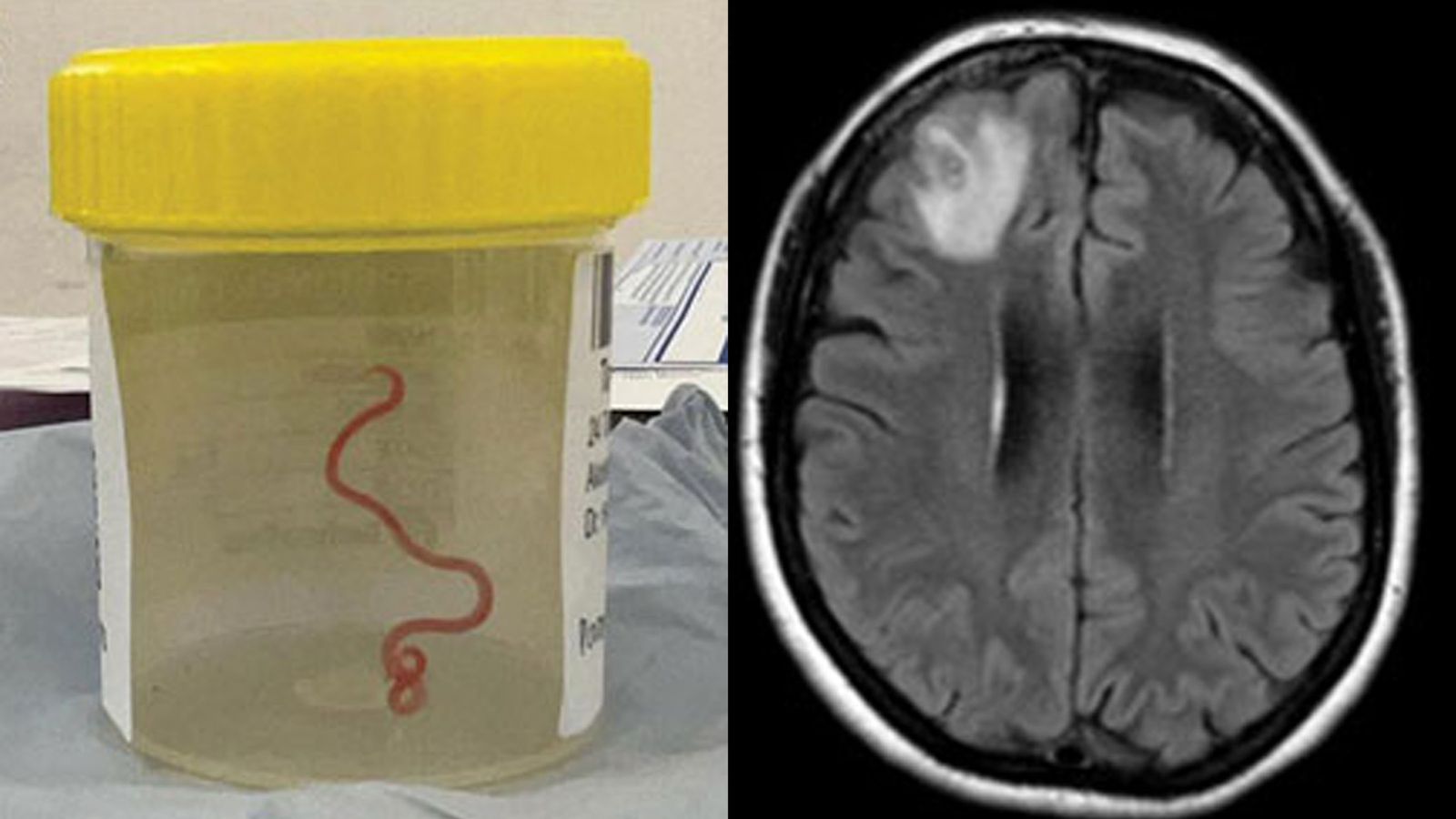
A woman who was experiencing forgetfulness and depression has had an 8cm-long parasitic roundworm removed from her brain.
The 64-year-old English woman, who was living in New South Wales, Australia, was admitted to hospital in January 2021 after three weeks of abdominal pain and diarrhoea, followed by a dry cough and night sweats.
By 2022, her symptoms had evolved to include forgetfulness and depression, prompting medical professionals to refer her to Canberra hospital.
An MRI scan of her brain revealed that a motile helminth – a parasitic roundworm – was living in the right frontal lobe lesion of her brain.
Surgical intervention became the only option, and doctors successfully removed the roundworm, which measured 8cm (80mm) in length and 1mm in diameter.
The neurosurgeon behind the surgery, Dr Hari Priya Bandi, spoke to Sky News describing the case as a “mystery” when it was first presented to her team.
After the scan was performed, Dr Bandi explained how a “distinct abnormality” was present in her brain which was rapidly changing over time.
Ukraine war latest: Speculation grows over Prigozhin funeral; Putin ‘unlikely’ to meet military recruitment target – despite offering big salaries
Luis Rubiales: Spanish football federation calls for president to resign over World Cup kiss
Who is Luis Rubiales – the Spanish FA boss at the centre of the World Cup kissing row?
She added: “It was certainly different to textbooks of parasites in the brain and no one had seen anything similar to this case.”
‘It was moving!’
During the surgery, Dr Bandi used forceps to lift the unknown entity from the brain and said: “To my shock there was a linear wiggling red line… We could see it was moving!
“[It was] surprising for us and not what we’re used to at all when we do such planned surgery… but [it was] an answer to this woman who had been suffering for so long.”
The woman was “pleased” to receive an explanation for her symptoms, according to the neurosurgeon who added that treatments were available despite the rarity of the case.
The worm’s fate
Dr Bandi said it was looked at by an infectious diseases specialist immediately after removal as well as a veterinary scientist who said: “That looks so red” – distinct of a nematode or roundworm.
The worm was taken to the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in Canberra where it was “still rapidly moving… and in three days’ time it was still wiggling quite happily”.
It was then “sliced for genetic typing”.
Identified as a third-stage larva of the Ophidascaris robertsi nematode species, the case is unprecedented in medical history, and has been documented in the journal of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Typically, this parasitic worm lives in the digestive tracts of carpet pythons indigenous to the Australian state of New South Wales.
Medical professionals suspect the woman inadvertently ingested the worm’s eggs by eating edible grasses that were tainted with snake faeces, however, the actual cause cannot be confirmed.
After the eggs hatched within her body, medics believe the larvae embarked on a journey to her brain. This could have been influenced by the medication she was taking, which compromised her immune system.
“We hypothesised that she inadvertently consumed eggs either directly from the vegetation or indirectly by contamination of her hands or kitchen equipment,” the medics said.
Ordeal began in 2021 – with evolving symptoms
The woman’s ordeal began in January 2021 when she was admitted to a hospital in Canberra.
Despite comprehensive tests, the results of her numerous medical tests remained inconclusive. Eventually, she received a diagnosis of pneumonia originating from an undisclosed source and was prescribed steroids.
Although her condition initially showed signs of improvement, she found herself readmitted to the hospital a few weeks later, plagued by a fever and an unrelenting cough.
Doctors suspected the presence of T-cell driven hypereosinophilic syndrome, a condition that can be life-threatening, characterised by the immune system going into overdrive. To address this, she was administered immunosuppressing medication as part of her treatment.
A CT scan also unveiled multiple troubling findings, including pulmonary opacities, hepatic and splenic lesions.
Three weeks later, her condition worsened, prompting her admission to a tertiary hospital. With persistent fever and cough, her medical team escalated the investigation.
By January 2022, she experienced further changes, including forgetfulness and worsening depression over a three-month period, prompting doctors to examine her brain.
Subsequent scans unveiled a brain lesion, leading to her undergoing surgery in June of the previous year.
‘String-like structure’ discovered in brain
During the surgical procedure, an unusual “string-like structure” was discovered within the lesion, and to doctors’ astonishment, it began to wriggle.
Examination of the worm indicated its affiliation with a family of parasites typically exclusive to snakes. This marked the first documented instance of such a parasite infecting a human.
Read more from Sky News:
Helicopter crashes into apartment building
Passengers stranded after air traffic control fault
Subsequent medical procedures revealed the absence of any additional worms residing within her body.
Half a year after the surgery, while the woman’s forgetfulness and depression had shown signs of improvement, they persisted to some extent.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free
Medical experts emphasised the significance of ongoing monitoring, as studies on rats have demonstrated that the worm’s eggs can endure within the body for over four years.
But they added that while the species of worm had been known to infect animals’ digestive systems, it had not been discovered in the brain of any species before.
The medics said that while the particular worm in question is exclusive to Australia, there are similar species located in other parts of the world, suggesting the potential for further occurrences in the future.
They also emphasised that the case underscored the persisting danger of zoonotic diseases transmitted between humans and animals.
Zoonotic diseases, which transfer from animals to humans, are frequently mentioned as potential triggers for pandemics.