Quick Take
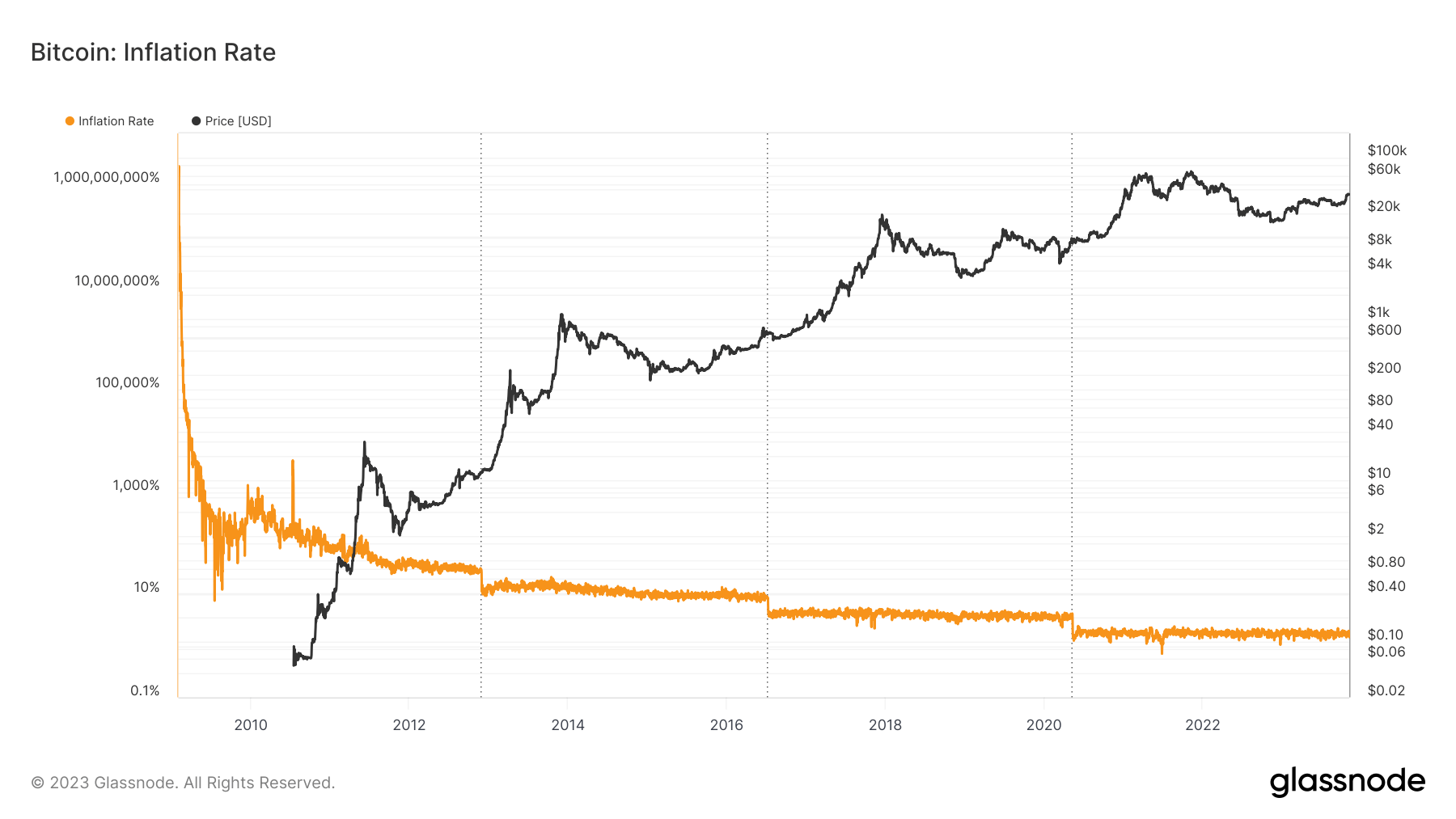
Bitcoin’s inflation rate, currently sitting at about 1.750%, is expected to reduce by half to approximately 0.875% upon the next halving in April 2024. The upcoming reduction in Bitcoin’s annual increase of supply created an interesting point of comparison with Ethereum, which experienced significant changes in its own rate after transitioning to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) last year.
Following the introduction of the London Hard Fork and the Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP-1559) in August 2021, a transaction base fee was established and burned, effectively reducing the ETH supply. This burn mechanism has destroyed an estimated 4.4 million ETH thus far, exerting deflationary pressure on Ethereum.
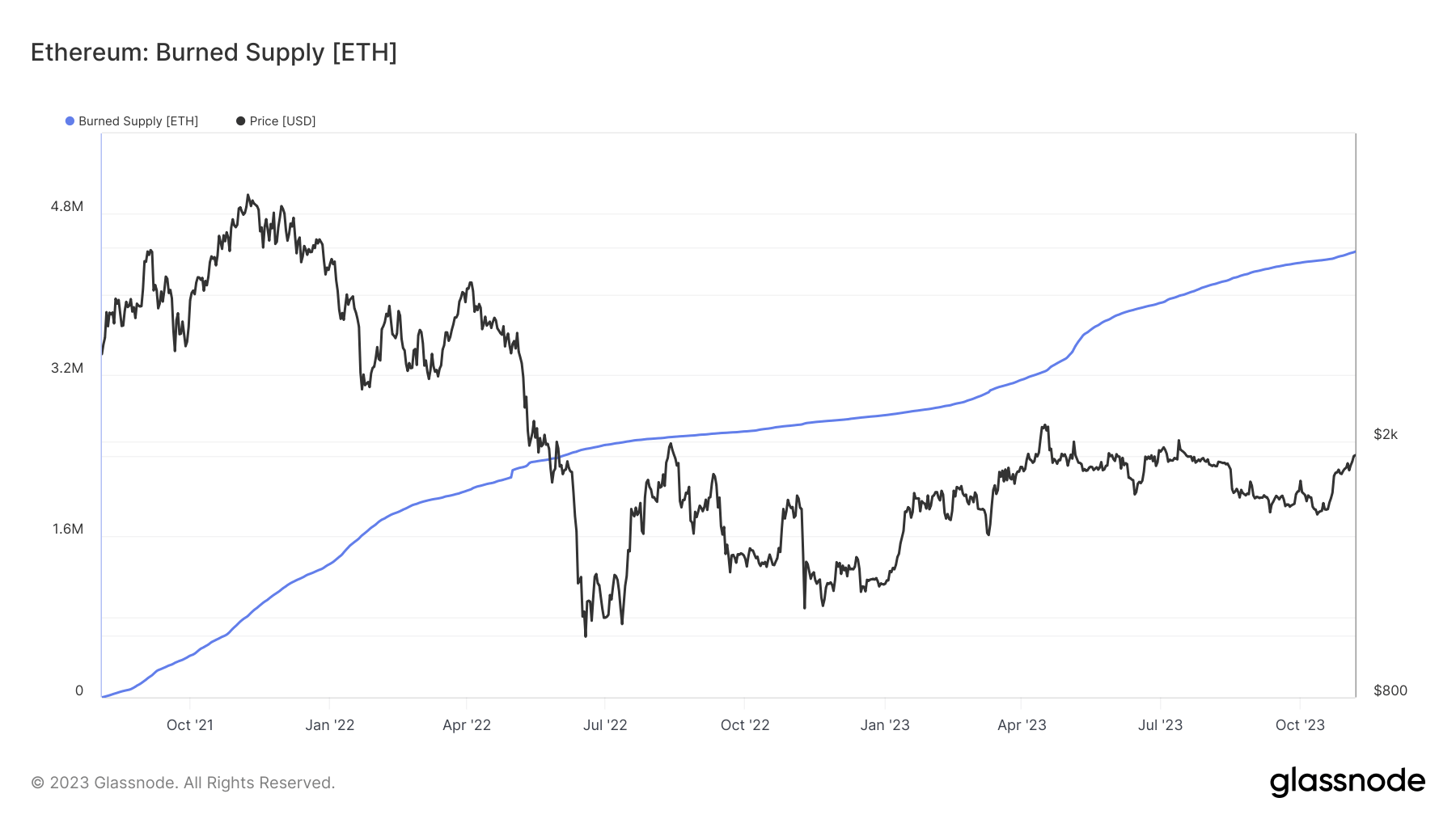
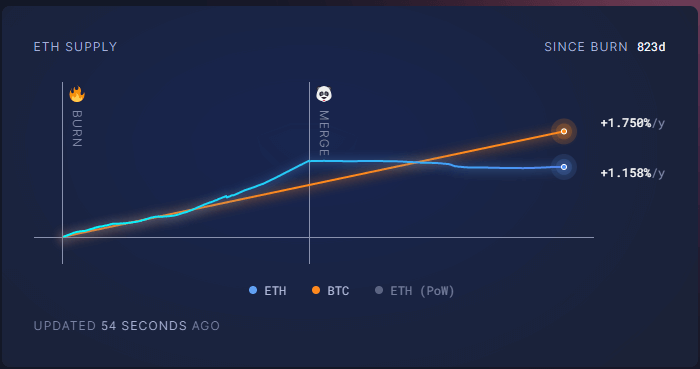
Since the burn mechanism was introduced 823 days ago, the annual increase in Ethereum’s supply has been around 1.158%. This was projected to continue following the Merge, a significant update that transitioned Ethereum from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a PoS consensus mechanism in September 2022.
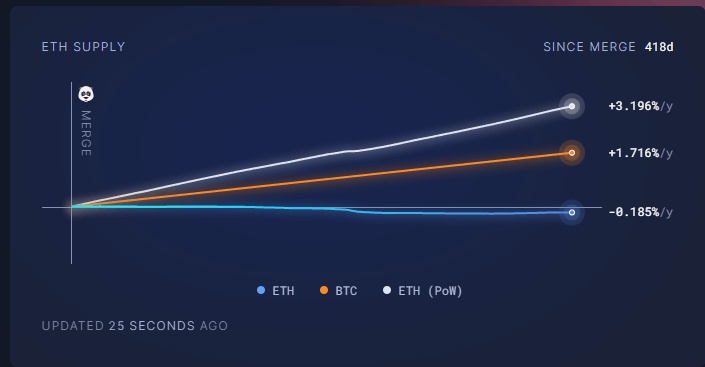
Following the Merge, Ethereum has registered a negative inflation rate of -0.185%, significantly lower than Bitcoin’s. Under the previous Proof-of-Work (PoW)mechanism, Ethereum’s inflation rate would have stood at around 3.196%.
However, if Ethereum maintains its current supply growth until April 2024, Bitcoin could exhibit a lower inflation rate following its halving.
The post Upcoming Bitcoin halving may put Ethereum’s inflation rate in the shadow appeared first on CryptoSlate.







